Development of Genetic Strategies to Interrogate Cancer Phenotypes
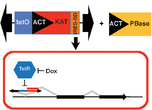 Figure 1. Design of a Mutagenic PiggyBac Construct.
Figure 1. Design of a Mutagenic PiggyBac Construct.
We developed and optimized a PiggyBac transposon-based technology that allows for the rapid genome-wide interrogation of the cancer genome for genes and pathways that can confer drug resistance. Because the transposon was an emerging technology, we focused our efforts on a model system that was more straightforward than CTCL. In particular, we applied this approach to human melanoma cell lines to identify the mechanisms of escape from targeted BRAF inhibitors.
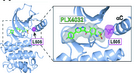 Figure 2. p.L505H Mutation Prohibits Binding of Vemurafenib in BRAF p.V600E
Figure 2. p.L505H Mutation Prohibits Binding of Vemurafenib in BRAF p.V600E
We performed a two-armed screen. We cultured unmutagenized melanoma cells continuously in the BRAF inhibitor, vemurafenib. We identified naturally occurring vemurafenib resistant melanoma cells. By exome sequencing, weidentified a second site mutation, p.L505H, that inhibits binding of vemurafenib on mutant BRAF. Satisfyingly, this mutation has recently been shown to occur spontaneously in patients who develop vemurafenib resistance (Hoogstraat, et al., Pigment Cell Melanoma Research (PCMR), 2015).
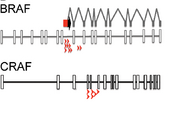
Figure 3. Common Insertion Sites in BRAFi-Resistant Melanomas.
In the other arm, we performed a forward genetic screen. We found that all of our transposon-dependent mutant cell lines harbored an insertion in either BRAF or CRAF. In our screen, all of the transposon insertions in the BRAF gene occurred in intron 8, which led to the transposon-dependent generation of a truncated BRAF protein. Our group and others found these mutations in clinical samples derived from patients with acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors. Therefore, Piggybac mutagenesis appears capable of identifying important genes, pathways, and splice variants that confer drug resistance.
Collectively, our studies support the use of pan-RAF inhibitors in melanomas resistant to BRAF inhibitors.
Reference: Choi, et al. 2014
Related Work by Our Lab in Melanoma Genetics:
Distribution of Mutations in Mucosal Melanomas and Dysplastic Nevi
Mutations in Asynchronous Melanoma Metastases.